Navigation

Related Post
Web Services
Web Services are software systems designed to support machine-to-machine interaction over a network. They allow different applications from various sources to communicate with each other without time-consuming custom coding.
These services are based on standardized protocols and formats such as HTTP, XML, and JSON, making them platform- and language-independent. In IT, Web Services play a crucial role in enabling integration between diverse systems, both within and across organizational boundaries. They are commonly used in enterprise applications, cloud computing, and API-based architectures.
Section Index
- Key Aspects
- System Interoperability
- Standard Protocols
- SOAP and REST
- Security Measures
- Performance Monitoring
- Conclusion
- What is a Web Service? – 7 mins
Key Aspects
- Web Services enable system interoperability across different platforms and programming languages.
- They rely on standard protocols, such as HTTP, and messaging formats, including XML and JSON.
- Web Services can be implemented using technologies such as SOAP and REST.
- Security is a critical component of Web Services, ensuring data integrity and access control.
- Monitoring and managing Web Services is essential for performance and reliability in IT environments.
System Interoperability
System interoperability is one of the main benefits of Web Services in IT. These services allow applications developed in different languages and operating on various platforms to exchange data seamlessly. This is particularly important in large organizations that use a mix of legacy systems and modern technologies. Web Services serve as a bridge that simplifies the integration of these disparate systems, improving overall operational efficiency.
Interoperability also enhances collaboration between business partners. For instance, a logistics system developed in Java can interact with a vendor’s inventory system written in .NET using Web Services. This seamless interaction enables real-time data sharing, facilitating better decision-making and faster responses to changes in business needs.
Standard Protocols
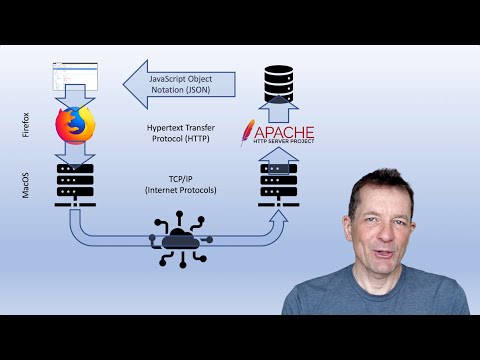
Web Services rely heavily on standard communication protocols, with HTTP being the most widely used. These protocols define how messages are formatted and transmitted between systems. Formats such as XML (Extensible Markup Language) and JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) are commonly used for structuring data within these messages, making it easier for different systems to parse and utilize the information.
By using standardized formats and protocols, Web Services avoid the need for custom integration solutions. This standardization reduces development time and costs while promoting consistency in the exchange of data. It also makes it easier for IT teams to maintain and troubleshoot integrations.
SOAP and REST
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) and REST (Representational State Transfer) are the two main architectural styles used to build Web Services. SOAP is a protocol that utilizes XML-based messaging and offers robust features, including built-in error handling and security. It is often used in enterprise environments that require strict standards and reliability, such as those in the financial services sector.
REST, on the other hand, is more lightweight and flexible, utilizing standard HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. RESTful Web Services are popular in web and mobile applications due to their simplicity and scalability. Technologies like AWS API Gateway and Microsoft Azure support both SOAP and RESTful implementations, providing organizations with flexibility in their development strategies.
Security Measures
Security is essential when implementing Web Services, especially when sensitive data is transmitted across networks. Common security practices include using HTTPS to encrypt data in transit, implementing authentication methods such as OAuth or API keys, and applying access control rules to restrict who can access the service.
In enterprise IT environments, tools such as IBM DataPower and WSO2 API Manager help enforce these security measures. These tools provide additional layers of protection, such as threat detection and message validation, to ensure Web Services are not only functional but also secure. Failing to secure Web Services properly can lead to data breaches and compliance issues.
Performance Monitoring
Monitoring Web Services is crucial for ensuring their availability and performance in production environments. IT teams use monitoring tools to track usage patterns, detect errors, and measure response times. These insights help identify bottlenecks and ensure that services meet their service-level agreements (SLAs).
Popular monitoring solutions, such as New Relic, Datadog, and Prometheus, provide real-time visibility into Web Services. They support alerting mechanisms to notify teams of issues before they affect users. Proper monitoring not only improves reliability but also supports proactive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs.
Conclusion
Web Services are a foundational technology in IT, enabling system integration and efficient communication between applications. Their use of standard protocols, secure architectures, and scalable designs makes them essential for modern IT operations.
What is a Web Service? – 7 mins