Navigation

Amazon Web Services – AWS
Standard Level
IT Tool
Related Post
Amazon Web Services – AWS
Amazon Web Services, or AWS, is a cloud computing platform provided by Amazon that offers a wide range of computing, storage, networking, and database services. It allows businesses and developers to access powerful IT resources over the Internet without owning or managing physical servers.
Through AWS, users can quickly launch applications, store large amounts of data, and scale their services up or down depending on demand. The platform supports a pay-as-you-go model, meaning users only pay for what they use. AWS has become a leading solution in IT for supporting web applications, data analysis, machine learning, and disaster recovery.
Full Profile
- Key Aspects
- Computing Services
- Global Infrastructure
- Security and Compliance
- Developer Tools
- Automation and Monitoring
- Conclusion
- Overview of AWS – 5 mins
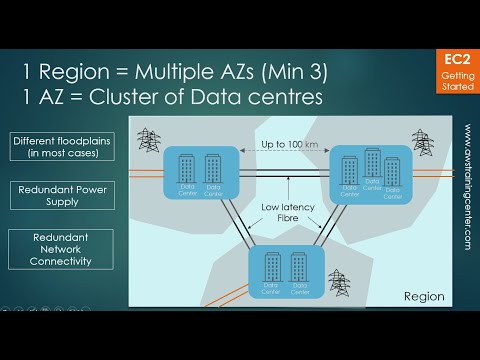
- Overview of Regions and Availability Zones – 11 mins
Overview of AWS – 5 mins

Overview of Regions and Availability Zones – 11 mins