Navigation

Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTPS
Advanced Level
IT Tool
Related Post
Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol – HTTPS
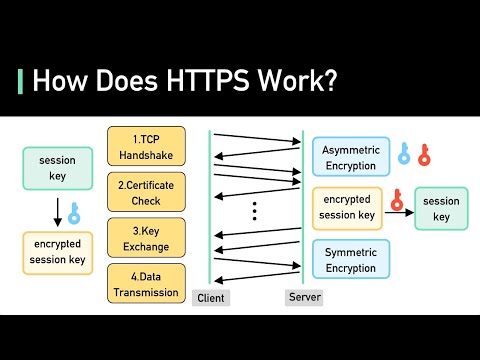
Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTPS) is an internet communication protocol that encrypts data between a user’s browser and a website. It is the secure version of HTTP, using encryption to protect the confidentiality and integrity of information.
HTTPS relies on Transport Layer Security (TLS) or its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), to prevent eavesdropping, tampering, and impersonation. It is a foundational element for secure online transactions, logins, and sensitive communications. Modern web browsers display HTTPS connections with a padlock icon, indicating that the site is verified and the data transmitted is encrypted, which is crucial for maintaining trust in digital services.
Section Index
- Key Aspects
- TLS/SSL Encryption
- Data Integrity
- Digital Certificates
- Secure Transactions
- Default Requirement
- Conclusion
- SSL, TLS, HTTPS Explained – 6 mins
SSL, TLS, HTTPS Explained – 6 mins